
Share this article
Share this article
Different organizations apply varying maintenance tips. Maintenance is not only required when a machine breaks down. It is vital to increase a machine’s lifespan and avoid future breakdowns. One of the most common types of equipment maintenance is condition based maintenance.
As the name suggests, condition-based maintenance is a machine servicing procedure done based on the condition of the machine or asset. Before the process begins, a thorough inspection is conducted and a review of past data.
Condition-based maintenance prevents future breakdown and improves the performance of the asset to increase productivity. Follow-up and monitoring the operations of the asset helps to schedule the best date to service the asset. With regular inspection, it is easy to identify problems.
Condition based maintenance, also known as CBM, can be defined as a servicing procedure that inspects the current condition of an asset, machine, or device and determines the type of repair it needs. The process entails replacement and repairs based on the machine’s health.

Condition-based maintenance provides a safer environment for machines to operate and prevents the likelihood for equipment to break down unexpectedly. Frequent maintenance can cause the machine to deteriorate at a faster rate. However, CBM helps to provide the most optimal servicing type of any asset, hence reducing the chances of damage.
Condition-based maintenance assists the repair and maintenance team in developing more accurate and informed decisions on machine maintenance. It also provides the correct information about how the organization can ensure long-term asset health and improve its maintenance processes and practices.
Risk-based maintenance focuses on the assets with the most risk if they fail. It determines the most economical use of resource maintenance. The main reason for this process is that the maintenance effort is optimized and minimizes the risk in case of failure.
Risk-based maintenance focuses only on assets with the most risks when they fail. In contrast, condition-based maintenance looks at the overall performance of a machine to ensure effective performance.
Risk-based maintenance focuses on reducing the risks in case a machine fails, while condition-based maintenance is used to determine what kind of repair an asset requires.
Meter-based maintenance is a service performed after a trigger on the meter reading. Most machines measure the number of hours worked, the distance covered or the number of parts produced, or the operating procedure such as flow rate.
Meter-based maintenance is planned, meaning it is a form of preventive maintenance and predictive maintenances. It is a complex form of maintenance since it requires one to read and interpret the meter reading. Meter-based maintenance helps organizations develop plans that are in conjunction with the organization’s operations. Firms that employ this type of maintenance can gain a higher level of control for their machines.
This maintenance type can only be successful if the correct maintenance schedule is implemented. The maintenance manager should capture vital information, analyze it, and develop sound decisions. The condition-based maintenance program is done every time one wishes to inspect and identify any probable equipment failure. It is also performed when one needs to schedule any incoming maintenance.
The overall benefits of condition-based maintenance include:
• Minimizes the cost of asset failure
• Improves asset productivity
• Reduces downtime due to unplanned failure
• Saves time spent on repair and maintenance after a breakdown
• Enhanced efficiency in maintenance practices and management
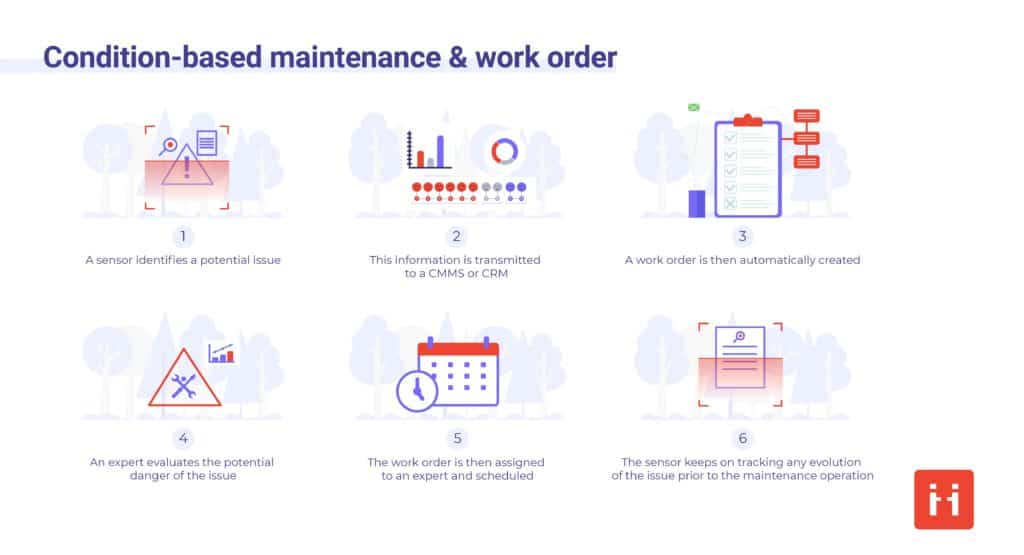
Some of the techniques for monitoring the status of machines are below:
• Vibration analysis: checking the vibration levels and carefully listening to the pattern, especially in machines that have rotating components
• Ultrasound is ideal for checking for any leaks
• Oil analysis to check the oil’s viscosity in machines that use oil for lubrication
• Infrared thermography helps detect heat waves and abnormalities such as insufficient heat or overheating
• Radiation analysis uses radiation imaging to identify internal problems in machines.
• Electrical monitoring applies the deviation principle in electrical parameters to identify problems within the machine’s internal parts
• A laser interferometer measures wave displacement changes using laser-generated and accurate light wavelength
• Electromagnetic Measurement involves measuring magnetic field distortions and eddy current changes to establish corrosion, cracks, and weaknesses
• Machine performance monitoring uses visual inspection and physical assessment to determine the proper functioning of any piece of machinery.
There are several types of technology and tools available to help determine the state of an asset. This information can then be used to general condition-based maintenance work orders.
Data collection increases the accuracy and effectiveness of the inventory procedures. Machine performance data provides more information on the general operation of the machine.
CBM involves machine inspection and monitoring using CMMS software. When performing this type of maintenance strategy, the inspection is conducted when the machine is working. To save time and reduce the resources needed, inspectors can use ViiBE visual support to conduct remote inspections with staff on-site. With the collaborative and AR features available, they can pinpoint potential issues that need further investigation without having to travel on-site themselves.
Modern machines have different kinds of sensors that help monitor the normal functioning of different parts. The sensors are controlled with different maintenance software to distribute data.
Condition-based maintenance helps to evaluate any worksite danger that is likely to occur. It works to avoid future problems by solving a predetermined issue.
Condition-based maintenance helps staff to develop work orders. The team can plan when to perform maintenance depending on the data collected. with ViiBE Report, anyone on-site that spots a machine malfunctioning can autonomously create a video report, adding notes, photos, and annotations. They can then assign a specific location or skill set to the report so that the CMMS system can use that information to create a work order for CBM.
When performing condition based maintenance CBM, one can easily schedule the appropriate repair and perform maintenance work.
CBM allows for real-time communication as data collected is analyzed directly by the repair team. With real-time visual support, technicians can ask questions and receive expert assistance when applying maintenance to a machine.

Machine vibration analysis involves inspecting the frequency of vibrations, mainly on rotating sections of machines. Any change from the normal is an indication of a problem.
Variations in heat signals indicate a likelihood for a machine to break down. When the temperature rises, it means that a particular bearing is about to fail, while a drop in temperature could be an indication of a leaking pipe.
This analysis helps to determine deep or subsurface faults. It measures inaudible sounds and converts them to audible pitch by the human ear.
Rotating parts will always produce a certain level of noise. During an acoustic analysis of machinery, variations in acoustic emissions could be an indication of known faults.
Debris found in the machine’s oil or lubricant could indicate material loss due to wear and tear. Proper analysis can help identify the main parts to replace.

Most machines have an optimal pressure at which they perform best. A slight pressure drop could lead to reduced performance, meaning there might be a problem with the hydraulic system requiring maintenance.
Electrical surges could cause problems in an asset or machine. Electrical analysis used pre-installed ammeters to help monitor the current flowing through the device. When the flow is abnormal, the team shuts down the machine and rectifies the minor problem before it blows to a significant electrical problem.
Condition-based maintenance is a non-disruptive maintenance schedule that helps reduce the overall cost of repair. It monitors the operation of any machine and identifies different parts that may require replacement. In addition, it helps improve the overall performance of the machine.
Free E-book available now!